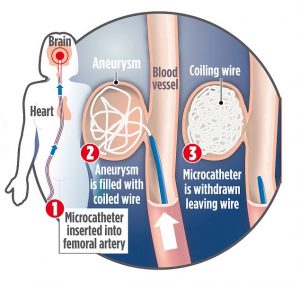
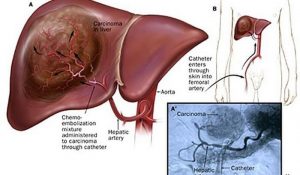
Techniques to open up a blocked tube like an artery, vein, bile duct, ureter, colon or oesophagus.
Another unique interventional radiology procedure is the Balloon Angioplasty and Stents, where a long catheter with balloon ends are used to remove the plaque from the affected area. This procedure is performed in the cardiac catheterization laboratory, also known as Cath lab. The balloons and stents are the best tools that can be used in the treatment of coronary artery disease or CAD. Usually, CAD cannot be managed by medicines. Therefore, balloons and stents technique works best for CAD.
The process involves a twist in the old fashion angioplasty. A long tube or catheter is designed with balloon-shaped tips. The balloons are inflated at the blockage site in the artery. This way, the plaque gets flattened, or even compressed, against the walls of the artery. This kind of angioplasty is also known as percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty or PTCA.
The balloon angioplasty is quite beneficial as it can be used to open the vessels, which has become narrow or has shrunk down in many parts of the human body. The stent is a minute mesh-like device used in modern interventional radiology. It is made up of substances with metallic nature. The stent acts as a support or scaffold in the interventional radiology procedures.
Usually, the stent is placed inside the coronary artery, which aids in keeping the blood vessel open. In this way, the stents help in improving the blood flow to the muscles of the heart, which eventually reduces the pain of angina.
The stents are usually built with balloon-like fixtures at the end of the tube or catheter. These kinds of angioplasty are found in more than 80 per cent of patients who get balloon angioplasty. Doctors use stents like this for body parts other than the heart as well. Stents can also be used in the medical procedure involving carotid arteries in the neck or the arteries in the aorta along with the peripheral arteries in the legs.
Doctors usually suggest their patients to avoid drinking or eating after midnight prior to the day these tests are conducted. In case a patient has diabetes, then it is essential to consult the doctor before undergoing the procedure; otherwise, it might affect the blood pressure of the patient. During the procedure, the doctor attaches a catheter that goes into the artery inside the heart. A video monitor is used to see the inside of the body. Once the doctor has detected the blocked area, a dye is injected into it. This helps the doctor to get a snapshot of the coronary arteries. This method is also known as a coronary angiogram.
Once the blocked area is detected, the doctor ties a thread, also known as guidewire around the artery. After that, the balloon tip is inflated in that area, which subsequently presses against the plaque, causing compression against the artery walls. The inflation and deflation of the balloon are done several times to compress the affected area. The stent also contains medicine, which avoids further spreading of the plaque.